www.darkzoo.net -> Trojan Carousel -> The GEEK CARD
Click here to return
to www.darkzoo.net
The GEEK
CARD : User Guide
Click here for printable version
.....If you don't have
a Geek card and you want one, just send stamped, self-addressed envelope to
..........Carl
Frederick
..........127
Pine Tree Road
..........Ithaca,
NY 14850
.....and
tell me how many you'd like (maximum of five, please). I'll send them right
off to you. (No charge, of course.)
Errata:
Card Front: The last character of the first line
of Morse Code should be -. and not .- (Thanks to Larry Hodges for catching it.)
The code symbol ...--- should have been ...--
(Thanks to Jaron Bernard and Alex Leaf)
Card Back: He in the table of elements should
be (boldface) He (Thanks to Ian Randal Strock)
NEPTUNE should be (boldface) NEPTUNE.
Thanks to Mike Brescia for finding an error on
this page, now corrected (description of G).

Click here to return to The Trojan Carousel page
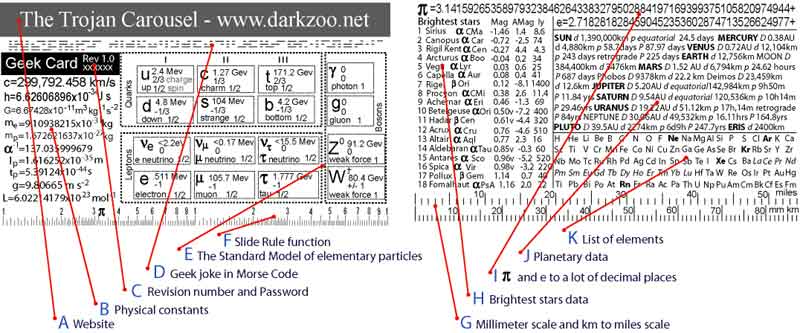
A Website
![]() (Click
to go to top of card image)
(Click
to go to top of card image)
.....www.darkzoo is the personal website of Carl
Frederick: physicist and science fiction author (me).
.....The Trojan Carousel, is a (geeky) novel available
to read for free. Actually, so that it not be considered web-published, only
the first half is up on the site. But, you may e-mail me for the rest of it
(darkzoo@darkzoo.net), and I'll send it to you. If you have a Geek Card though,
you can enter the card password (with user name card
) and read it all on the web (fiction on a password protected site is generally
considered not web-published). See item C below.
B Physics
constants ![]()
.....c
The speed of light
.....
The speed of light in a vacuum is given in kilometers per second. The constancy
of c regardless of whether the observer is speeding toward or away from the
light source, was a paradox in classical physics. The paradox remained until
Einstein resolved it with his Special Theory of Relativity.
.....h
Planck's constant
..... Plank's constant is given in units
of Joule*seconds. A Joule is a unit of energy. 1 J = 1 kg * (meter squared/second
squared). The constant was first used in the study of black-body radiation where
the relationship energy = h * frequency, was deduced for photons. The uncertainty
principle also has h in it. One aspect of the principle says the uncertainty
in a particles position * the uncertainty in its momentum must be greater than
h / (4 * pi). The interpretation of this is that a particle doesn't have
a well defined position and momentum at any given time. h pervades quantum mechanics.
Indeed, if one could reduce h to zero (impossible), quantum mechanics would
reduce to classical mechanics.
.....G
The gravitational constant
.....In
Newton's theory of gravitation (a pretty good theory), the (gravitational) force
between two masses, m, and M, is G*m*m/(r squared) where r is the distance between
the masses. So, for example, for masses of one kilogram and a separation of
one meter, the force between the masses would be G Newtons. (A Newton is a kilogram
meter per second squared.)
.....me
The mass of the electron
.....mp
The mass of the proton
.....The masses of the proton and electron
are given in kilograms. The ratio of the proton to the electron mass has been
measured. The ratio, called beta, is around 1836.152701
.....The
inverse of the fine structure constant alpha
.....The
fine structure (coupling) constant represents the strength of the electromagnetic
force. (The much used inverse of alpha is an historical artifact, since it was
at one time thought to be exactly equal to 137.) It is called 'the fine-structure
constant' because it is related to the fine-structure observed in atomic spectra.
.....lp
The Planck length
.....Planck noted the importance of the
three constants c, G, and h. He also noted that apart from numerical factors,
there is a unique way of using these constants to derive units of length, time,
and mass. For length, one has the square root of (h*G/c cubed). [In actuality,
one uses h-bar rather than h. h-bar is just h divided by two pi.] It may well
be that any length smaller than the Planck length has no physical meaning. (For
you physicists out there, it should be noted that for a particle of the Planck
mass, the Schwarzschild radius becomes equal to the Compton wavelength. And
that length turns out to be the Planck length.]
.....tp
The Planck time
.....The
Planck time is the amount of time it would take light to traverse the Planck
length. It could well be considered a quantum of time in that any shorter interval
of time might not have any physical meaning.
.....g
The acceleration due to gravity (at sea level)
.....If, for example,
an apple were to drop from a tree, it would fall with an acceleration of g meters
per second per second (which is roughly 32 feet per second per second).
.....L
Avogadro's number (also known as Loschmidt's constant)
.....If you take
the molecular weight of a substance (the sum of the weights of the atoms which
make up the molecules [roughly equal to the number of protons and neutrons in
the atom], then the number of molecules in that many grams of the substance
will be L. For example, the molecular weight of carbon-12 is 12.0108. So 12.0108
grams of carbon-12 would contain L molecules.
C Revision
number and Password ![]()
.....This card is Rev 1.0. I'm sure there'll
be further versions (I invite suggestions as to what to include in later revisions).
Below the Rev number is the card password (here Xed out). The password gives
access to restricted parts of my website--in particular (if I can get editors/publishers
to allow it) to stories before they are published. In addition, where a non-geek
must send an e-mail request for the second half of 'The Trojan Carousel', a
card holder can simply enter the password and then read the second half on-line.
(The user name is card.) You can get to the restricted
area of the website by clicking on the center of the 'cat-eyed wolf' shield
on the homepage.
D Geek
joke in Morse Code ![]()
.....
This joke (transcribed into Morse Code) has a punch line that probably would
only be understood by computer geeks. I won't spoil anyone's fun by decoding
it here.
E 'The
Standard Model' of elementary particles ![]()
.....
The model describes matter and interactions as we understand them today. The
most fundamental components according to the model, are quarks (of six varieties),
Leptons (neutrinos, electrons, muons, and tau particles), and the force carrying
bosons (photons, gluons, Z and W particles). The familiar proton, for example,
is comprised of two u (up) quarks and a d (down) quark. The I, II, and III refer
to the so-called 'generations' The first generation makes up the common particles
(electrons, protons, neutrons, etc). Generation II particles are correspondingly
heavier than generation I particles. And they are unstable: decaying quickly
to generation I particles. Generation III particles are much much heavier than
their generation II counterparts, and also are unstable. The energy (mass),
charge, and spin are shown to the right of each particle.
F Slide-rule
function ![]()
.....
Should you find yourself without your calculator and are experiencing computation
withdrawal symtoms, you might find the card useful: The slide rule scale is
accurate and functional. Here is how you can use it to multiply two numbers
(you will need a sheet of paper or an index card):
I- Place the index card beneath the card with the left edge lined up with the
1 on the far left of the scale.
II - Let's suppose the two numbers you want to multiply are 3.5 and 4. With
the index card placed as in I above, put a pencil mark on the index card at
the top edge just under 3.5 on the scale (just to the right of pi on the scale).
III - slide the index card to the right until the left edge is just under 4
on the scale.
IV - The answer to the multiplication problem is now just above the mark on
the index card.

For division, proceed instead as follows:
Place the left edge of the index card under the denominator (the bottom number).
Put a mark on the index card directly under the value of the numerator.
Slide the index card to the left so that the left edge is directly under the
leftmost 1 on the slide rule scale.
The answer (quotient) will be directly above the mark.
G Millimeter
scale and km to miles conversion scale ![]()
.....At
the bottom of the card is a millimeter scale--which is also used for kilometer
to mile conversion. If you read the bottom scale as kilometers, you can use
the scale above it to convert to miles. For example, notice that 50 kilometers
is almost exactly 31 miles.
H Data
on the 18 brightest stars ![]()
.....The
18 brightest stars are listed in order of their visible magnitude (brightness).
Their absolute magnitudes are given as well, as are also their distances from
the Sun in light years.
(A star's absolute magnitude is the visual magnitude if the star were placed
at a distance of 10 parsecs. A parsec [parallax-second] is about 3.27 light
years. It is the distance where the star would subtend a parallax angle of one
second where the baseline is 2 AUs [an AU {Astronomical Unit} is the mean distance
from the Earth to the Sun].)
....Both the common and the scientific
names of the stars are given. The scientific name is (usually) a greek letter
(generally in order of the star's brightness in its constellation) followed
by the name of the constellation. When speaking of the star using the scientific
name, generally one uses the genitive case (possessive case) of the constellation
name. For example, Sirius, alpha in the constellation of Canis Major, would
be referred to as Alpha Canis Majoris. The abbreviations for the constellations
are used in the card. The full constellation names (and the genitives), are
as follows:
CMa = Canis Major (Canis Majoris)
Car = Carina (Carinae)
Cen = Centaurus (Centauri) [note: the star Rigil Kent is more commonly known
as Rigel Kentaurus]
Boo = Bootes (Bootis)
Lyr = Lyra (Lyrae)
Aur = Auriga (Aurigae)
Ori = Orion (Orionis)
CMi = Canis Minor (Canis Minoris)
Eri = Eridanus (Eridani)
Cru = Crux (Crucis)
Aql = Aquila (Aquilae)
Tau = Taurus (Tauri)
Sco = Scorpius (Scorpii)
Vir = Virgo (Virginis)
Gem = Gemini (Geminorum)
PsA = Piscis Austrinus (Piscis Austrini)
I Pi and
e to lots of decimal places ![]()
.....It is extremely unlikely
that you will ever need pi to 60 decimal places. But some geeks like to memorize
large number of digits of pi. So here it is then--in case you feel the desire
to do some memorization.
.....Pi,
of course, is the ratio of the circumference to the diameter of a circle. The
number is irrational (i.e. is not the quotient of two integers), and indeed
is transcendental (i.e. irrational and also not a solution of any polynomial
equation with rational coeficients).
.....e
is another transcendental number. It is the base of the natural logarithms.
It is an important number in the mathematics of probability and decay.
J Data
on the Sun and planets ![]()
.....Information
on the diameters, distances, and periods of rotation and revolution are given
for the Sun, planets, two dwarf planets (Pluto and Eris), and a few of the planetary
satellites. The abbreviations used are as follows:
d = diameter
D = distance from the Sun in Astronomical Units (An AU is the mean distance
from the Earth to the Sun. About 93 million miles). In the case of the planetary
satellites, D = the distance to the center of the satellite's planet.
p = the length of the day
P = the length of the year
K List
of natural elements ![]()
.....
This 20-column listing of the first 100 atomic natural elements has the inert
gasses in bold and the 'rare earths' (lanthanides) in italics. Knowing this,
a chemistry geek should be able to reconstruct the elements in periodic table
form. The international symbols for the elements are used. Below is the list
using the element names:
Hydrogen Helium Lithium Beryllium Boron Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen
Flourine Neon Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Silicon Phosphorus
Sulfer Clorine Argon Potasium Calcium
Scandium Titanium Vanadium Chromium Manganese Iron Cobalt Nickle Copper Zinc
Gallium Germanium Arsenic Selenium Bromine Krypton Rubidium
Strontium Yttrium Zirconium
Niobium Molybdenum Technetium Ruthenium Rhodium Palladium Silver Cadmium Indium
Tin Antimony Tellurium Iodine Xenon Cesium Barium Lanthanum
Cerium Praseodymium Neodymium
Promethium Samarium Europium Gadolinium Terbium Dysprosium Holmium Erbium
Thulium Ytterbium Lutetium Hafnium Tantalum Tungsten Rhenium Osmium Iridium
Platinum Gold Mercury
Thallium Lead Bithmuth Polonium Astatane Radon Francium Radium
Actinium Thorium Protoactinium Uranium Neptunium Plutonium Americium Curium
Berklium Californium Einsteinium Fermium